You can easily determine how much house you can afford by following a few general guidelines:
Your monthly mortgage payment, including principal, interest, real estate taxes and homeowners insurance, should not be more than 28 percent of your gross monthly income (before taxes). This is your housing expense ratio.
Ideally, your total monthly debt obligation should not exceed 36 percent of your gross income, though exceptions are sometimes made. Total debt includes the mortgage payment plus other obligations such as car loans, child support and alimony, credit card bills, student loans, and condo association fees. This is your debt-to-income ratio.
For example:
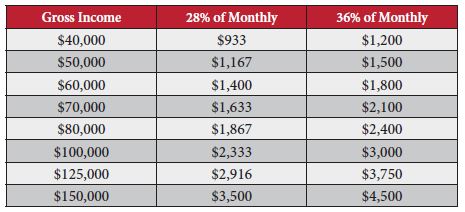
The maximum amount of money available for a monthly mortgage payment at 28% of gross income, for a home buyer who makes $40,000 a year, would be $933. However, the total debt payments each month should not exceed 36%, which comes to $1,200.
The following chart may help you see what your maximum monthly debt payments should be based on your annual gross salary:
To help you figure out what you can afford, list all your monthly expenses out. If it’s a joint application, combine the expenses.
Next, figure out your total monthly income after taxes, and subtract the total monthly expenses. This leaves you with the total amount available to use toward your future home loan.
Your Savings
Your home-buying budget is the amount you can borrow, plus whatever savings you can contribute. In some situations you can obtain a loan with no down payment, however, it’s important to note that if you want to borrow more than 80% of a home’s value, you may be required to pay Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI). It’s an additional payment amount that covers the bank should you have trouble repaying your loan.






